
Images/mathematical drawings are created with GeoGebra.

#Reflection rules geometry calculator how to
how to reflect an object using a transformation matrix. The general rule for a reflection in the yx . how to reflect points and shapes on the coordinate plane using the Coordinate Rules.
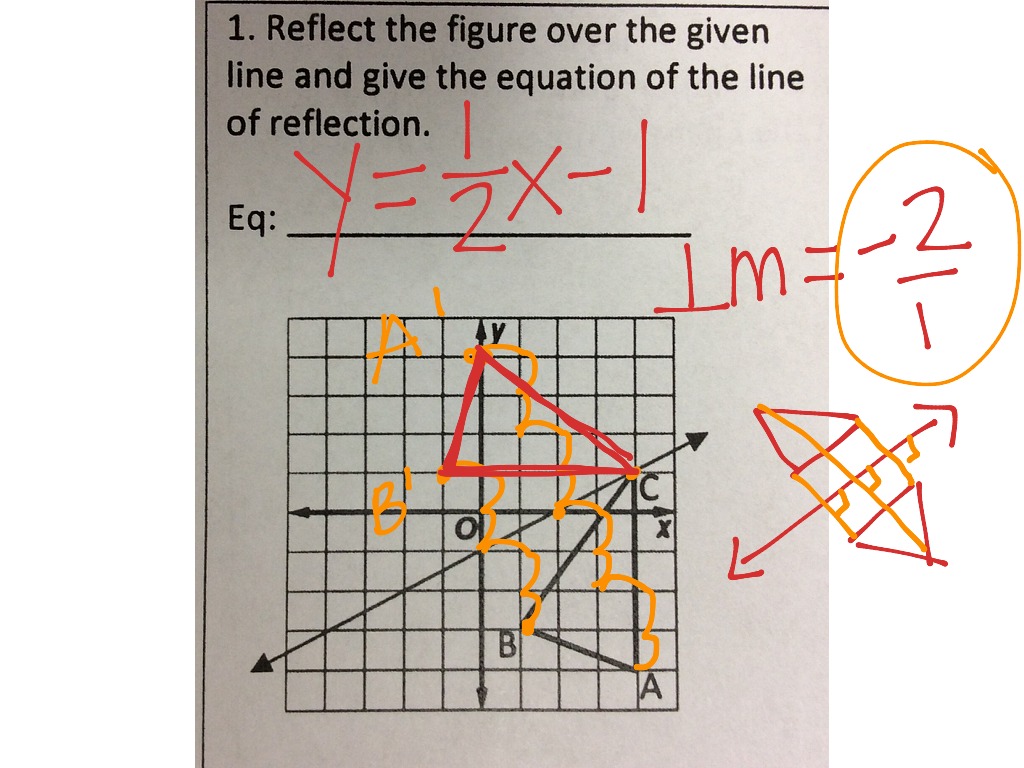
$A=(0, -2)$, $B=(-2,-2)$, $C=(-2,-4)$, and $D=(0,-4)$ī. A reflection in the line y x can be seen in the picture below in which A is reflected to its image A. Then, go to your Google Classroom and complete the Reflection Rules form describing the change in the coordinates. See how the coordinates between the original and reflection change. When the square is reflected over the line of reflection $y =x$, what are the vertices of the new square?Ī. Then, move the mirror line around to see how the coordinates of the original (preimage) and the reflection (image) relate.
#Reflection rules geometry calculator free
Free math problem solver answers your calculus homework questions with.

Suppose that the point $(-4, -5)$ is reflected over the line of reflection $y =x$, what is the resulting image’s new coordinate?Ģ.The square $ABCD$ has the following vertices: $A=(2, 0)$, $B=(2,-2)$, $C=(4, -2)$, and $D=(4, 0)$. Discontinuity stress Appendix 4 gives definitions and rules for stress analysis. Use the coordinates to graph each square - the image is going to look like the pre-image but flipped over the diagonal (or $y = x$). This means that the image of the square has the following vertices: $A=(3, -3)$, $B=(1, -3)$, $C=(1, -1)$, and $D=(3, -1)$. In this activity, students explore reflections over the x-axis and y-axis, with an emphasis on how the coordinates of the pre-image and image are related. Conditions are free-field and there is no reverberant field.The $\boldsymbol Math Solver includes a lot of mathematics topics such as geometry, analytic geometry, equations and inequalities.Walls used in the model are considered to be perfectly reflecting and at 1 metre distance (facade level).The noise source behaves as a point source and is far-field, where inherent directivity is minimal.We’ll be using the absolute value to determine the distance. Since it will be a horizontal reflection, where the reflection is over x-3, we first need to determine the distance of the x-value of point A to the line of reflection. There are no affecting weather conditions, such as wind or temperature inversion, as these will affect the propagation path of a noise source and diffraction around the barrier. This is a different form of the transformation.In reality when dealing with short distances and many reflective surfaces the "canyon effect" may occur with repeating reflections. Directions: Without a calculator, give the name of the parent function. Brewsters Angle Calculator, you can estimate the angle at which reflected light. There are no reflections from the barrier. only vertically translated, horizontally translated, and/or reflected over the. If you forget the rules for reflections when graphing, simply fold your paper along the x-axis (the line of reflection) to see where the new figure will be.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
